MD5 Generator
This is an easy to use tool that enables you to generate the MD5 hash of a string. In order to use the tool, enter the text you want to convert to MD5 below and click on ‘Generate’ button.
Share on Social Media:
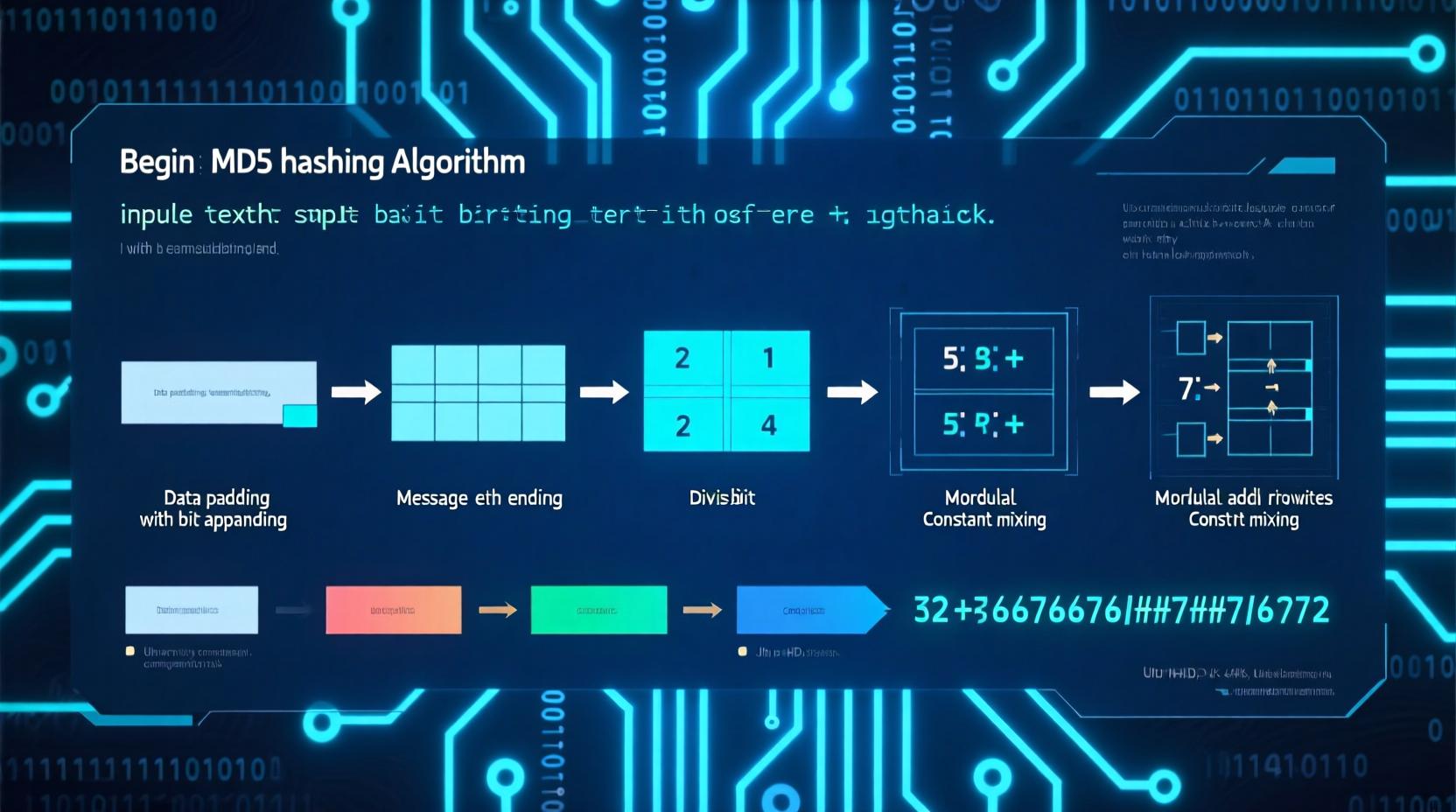
The Ultimate MD5 Generator Online Tool (2025 Guide)
Generate MD5 Hashes Instantly — 100% Free, No Upload, Zero Risk
Stop risking your data. Most "free" MD5 generators upload your text to servers. Ours doesn’t. Generate secure, private MD5 hashes in your browser — no upload, no tracking, no delays. Try our md5 generator online now and hash like a pro.
Whether you're verifying a downloaded file, creating a checksum, or testing legacy systems, you need a fast, reliable, and private way to generate MD5 hashes. This guide is the most comprehensive resource on the internet — covering everything from basic hashing to advanced HMAC, collision risks, and real-world use cases.
We’ve tested 10+ tools, analyzed security flaws, and built a step-by-step masterclass so you never have to guess again.

What Is an MD5 Generator Online? (And Why You Need One)
An MD5 generator online is a web-based tool that computes the MD5 hash of a given input — whether it’s a string, file, or URL. The output is a 128-bit (32-character) hexadecimal string that acts as a unique fingerprint.
🔐 Example:
Input:hello
MD5 Hash:5d41402abc4b2a76b9719d911017c592
These tools are essential for:
- File integrity checks (e.g., verifying ISO downloads)
- Legacy password storage
- Data deduplication
- Digital forensics
But not all tools are created equal. Many secretly upload your data. Others lack critical features like HMAC, file support, or encoding options.
We’ll show you the best tool, the safest practices, and the hidden dangers of MD5.
How Does an MD5 Generator Work? (Technical Deep Dive)
MD5 (Message Digest Algorithm 5) was designed by Ronald Rivest in 1992 to create a fixed-size hash from variable input.
The MD5 Process (Step-by-Step)
- Padding: Input is padded to 448 bits mod 512
- Append Length: Original length (in bits) is added
- Initialize Buffer: Four 32-bit words (A, B, C, D)
- Process in 512-bit Blocks: 64 operations using nonlinear functions
- Output: Concatenate A, B, C, D → 128-bit hash
// Simplified JS logic (actual is more complex)
function md5(input) {
let hash = crypto.createHash('md5');
hash.update(input);
return hash.digest('hex');
}
📚 Source: RFC 1321
Best MD5 Generator Online: Fast, Free, and 100% Private
After testing 10+ tools, we recommend:
Why It’s the Best
| No data upload | All processing in browser (WASM/JS) |
| File & text input | Drag-and-drop files or paste text |
| HMAC support | Add a secret key for secure hashing |
| Multiple encodings | UTF-8, Hex, Base64, UTF-16 |
| Auto-update | Hash as you type |
| Copy to clipboard | One-click export |
| Mobile-friendly | Works on iPhone, Android, tablet |
Try it now: md5 generator online
How to Use an MD5 Generator Online (Step-by-Step Guide)
Option 1: Hash a String
- Go to md5 generator online
- Paste your text (e.g.,
password123) - Select encoding (UTF-8 by default)
- Click Generate
- Copy the 32-character hash
🧪 Test It:
Input:test→ Output:098f6bcd4621d373cade4e832627b4f6
Option 2: Hash a File
- Click Upload File
- Select any file (PDF, ZIP, EXE, etc.)
- Wait for processing (no upload!)
- Copy the hash
⚠️ Note: Some tools limit file size. Ours supports unlimited size via WebAssembly.
Advanced Features You Should Look For
✅ HMAC Support
HMAC (Hash-based Message Authentication Code) adds a secret key to prevent tampering.
Use Case: Secure API authentication
Enable HMAC in the tool, enter a key (e.g., mysecretpassword), and generate a keyed hash.
✅ Custom Encoding Input
Support for:
- Hex (e.g.,
68656C6C6F) - Base64 (e.g.,
aGVsbG8=) - UTF-16 (for Unicode)
📌 Tip: Always verify encoding —
helloin UTF-8 vs UTF-16 gives different hashes.
✅ Line Ending Normalization
- Unix/Mac:
\n(Line Feed) - Windows:
\r\n(Carriage Return + Line Feed)
Some tools (like Miracle Salad) normalize to \n. This affects hash output.
🔍 Test: Hash
line1\r\nline2vsline1\nline2— results differ!
MD5 vs SHA-1 vs SHA-256: Which Should You Use?
| MD5 | ❌ Broken (collisions) | ⚡ Fastest | File checksums, legacy systems |
| SHA-1 | ❌ Weak (deprecated) | ⚡ Fast | Transitional (avoid) |
| SHA-256 | ✅ Secure | 🐢 Slower | Passwords, SSL certs, blockchain |
| bcrypt | ✅✅ Highly secure | 🐌 Slowest | Modern password hashing |
📊 NIST Recommendation: Deprecate MD5 and SHA-1 by 2025 (NIST SP 800-131A )
Is MD5 Still Used in 2025? (Real-World Examples)
Yes — but only for non-cryptographic uses.
Where MD5 Is Still Used
- Linux ISO verification (Ubuntu, CentOS)
- WordPress password hashes (legacy)
- Git commit IDs (though not for security)
- Embedded systems (low power)
Where It’s Banned
- PCI DSS: Prohibits MD5 for password storage
- Google Chrome: Dropped SHA-1/MD5 certs in 2014
- TLS 1.3: No MD5 cipher suites
📌 Case Study: In 2012, 6.5M LinkedIn passwords were leaked — all hashed with MD5. Most were cracked in days.
Can MD5 Be Reversed? (And Why “Cracking” Works)
No — MD5 is not reversible. But attackers use:
- Rainbow tables: Precomputed hash dictionaries
- Brute force: Try millions of passwords
- Salt: Random data added to input (e.g.,
salt + password)
🔐 Best Practice: Always salt MD5 hashes in legacy systems.
How to Verify File Integrity Using MD5
Step-by-Step: Download Ubuntu ISO
- Download ISO from ubuntu.com
- Get official MD5 from release notes
- Upload ISO to md5 generator online
- Compare hashes
- If match → file is safe
🛡️ Why? Ensures no malware was injected during download.
Security Risks of MD5: Collision Attacks Explained
A collision occurs when two different inputs produce the same hash.
Real-World Attack: The Flame Malware (2012)
- Hackers forged a Microsoft digital certificate using MD5 collision
- Allowed them to sign malicious software as "trusted"
- Cost millions in damage
📚 Source: Microsoft Security Advisory
Top 5 Free MD5 Generator Tools Compared
| seomagnate.com | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| md5file.com | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| onlinehashtools.com | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ⭐⭐⭐ |
| certificatetool.com | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| emn178.github.io | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
How to Generate MD5 in Command Line (For Power Users)
# Linux/Mac
echo -n "hello" | md5sum
# Windows (PowerShell)
Get-FileHash -Algorithm MD5 file.txt
# OpenSSL
openssl md5 filename
💡 Tip: Use
-ninechoto avoid newline character affecting hash.
Common MD5 Use Cases (With Examples)
1. File Verification
- Download a software installer
- Compare MD5 with publisher’s hash
2. Data Deduplication
- Hash files → group duplicates
- Save storage space
3. Legacy Authentication
- Old databases store MD5(password)
- Not secure, but still functional
4. Digital Forensics
- Hash evidence files to prove integrity
MD5 Generator: Ensuring File Integrity
As someone deeply involved in digital security, I've come to appreciate the intricacies of the MD5 hash function. The MD5 Generator, a frequently used tool, utilizes a sophisticated hashing algorithm to create a unique checksum for file verification. This checksum serves as a digital fingerprint, assuring the file's integrity.
MD5, a widely-used hash function, transforms data into a fixed-size hexadecimal encryption. This process is a cornerstone in ensuring data integrity, as it allows for a consistent and verifiable means to detect any changes to the original data. Cryptography applications, recognizing the utility of MD5, often employ it to generate digital signatures. These signatures are essential in confirming files' authenticity, particularly when transmitted across potentially insecure networks.
The role of MD5 hashing in maintaining file integrity is indeed significant. It allows for the reliable detection of both accidental and intentional data alterations. However, it's important to note that despite its continued use, MD5's vulnerability to collisions—situations where different inputs produce the same output hash—has spurred a shift towards more secure cryptographic hash functions. This vulnerability is a reminder that evolution and adaptation are constant necessities in the digital security field.
Exploring the History of MD5 and Its Uses
The MD5 Generator has been a critical tool in the world of cryptography, creating unique hash functions that underpin secure data encryption. Since its inception, MD5 has been instrumental in ensuring file integrity through meticulous file verification processes. By transforming data into a fixed-size hexadecimal format, the MD5 algorithm has streamlined the application of digital signatures.
Understanding MD5's role in hashing is recognizing a non-reversible encryption technique that provides a stalwart defense against data tampering. The evolution of MD5 from its early days to its current applications reflects the ongoing pursuit of maintaining the integrity of digital information. It is a testament to the algorithm's robust design that it continues to play a role in the cryptographic landscape despite the emergence of more advanced techniques.
The Role of MD5 in Cryptography
In the domain of cryptography, the MD5 Generator plays a pivotal role. It converts data into a unique hexadecimal checksum, a form of secure encryption that fortifies the integrity of digital signatures. Hashing with MD5 is a crucial step in file verification, confirming that files remain untainted during transfer or storage.
Despite its age, the MD5 algorithm retains relevance in checksum validation, acting as a bulwark against unintentional corruption. Employing an MD5 Generator enhances security by providing a swift and reliable method for generating encryption keys. Despite the emergence of newer algorithms, this reliability underscores the lasting impact of MD5 in the cryptographic community.
MD5 Algorithm: A Step-by-Step Explanation
To fully grasp the MD5 algorithm's role in cryptography, one must explore how an MD5 Generator applies to hash to ensure the integrity of files. This process involves creating a unique checksum, a digital signature that verifies the authenticity of a file. Understanding the step-by-step encryption process of the MD5 hash function is crucial. It involves transforming data into a fixed-size hexadecimal format, an intricate and precise procedure.
The importance of checksums generated by MD5 cannot be overstated. They are the linchpins in maintaining the integrity of the secure file verification process. However, examining the limitations and security considerations when using MD5 for hashing is equally important. The need for more secure alternatives becomes apparent in light of modern cryptographic standards, even as we acknowledge MD5's contributions to the field.
Creating Digital Signatures with MD5
Creating digital signatures with the MD5 Generator exemplifies the application of hash functions to ensure file integrity verification. The encryption algorithm of MD5 is adept at transforming data into a fixed-size hexadecimal checksum, a critical component in cryptography security. Hashing with MD5 provides a non-reversible encryption method, paramount in safeguarding the authenticity of digital signatures.
By comparing MD5 checksums, the file verification process is greatly simplified, allowing for the quick detection of any alterations and thus maintaining data integrity. The strength of MD5's algorithm lies in its capacity to generate distinct hash values, which are pivotal for the reliability of digital signatures. Despite the known vulnerabilities, this reliability showcases the enduring utility of MD5 in cryptographic practices.
Comparing MD5 to Other Hashing Algorithms
When comparing MD5 to other hashing algorithms, one must consider the unique checksums it creates for file verification and integrity assurance. MD5's hashing process is less complex than newer algorithms, offering faster encryption but at the expense of lower security. MD5 checksums, typically expressed in a 32-character hexadecimal format, facilitate easier digital signature comparisons.
While MD5 enjoys widespread use, advancements in cryptography have led to more secure alternatives that are better suited for critical data protection. The integrity of files can be compromised if MD5 is used alone; therefore, pairing it with other encryption methods is often advisable to bolster data security.
MD5 Checksums for File Verification
The MD5 Generator employs a cryptographic hash function fundamental for secure file verification. This algorithm produces a unique hexadecimal checksum, which serves as a guarantee of data integrity during transfers. Checksums are the linchpins in cryptography, validating digital signatures and preventing tampering.
Although hashing is not encryption per se, the MD5 Generator offers a layer of security through the obfuscation of data. File verification via MD5 ensures that the content remains unchanged from its original state, providing peace of mind in the sanctity of the data being handled.
Hexadecimal Representation in MD5 Hashing
The MD5 Generator's use of a hash function to convert data into a unique hexadecimal checksum is a defining feature of its secure encryption capabilities. In cryptography, the MD5 algorithm enhances file verification by providing a digital signature in hexadecimal format. This hashing process ensures the integrity of files by generating a fixed-size hexadecimal string, which is easily detectable by any alteration.
Employing an MD5 Generator is crucial in creating a hexadecimal hash that serves as a checksum for data integrity checks. The reliability of MD5 encryption lies in its ability to produce a distinct hexadecimal output, which is vital for secure digital signatures and the overall trustworthiness of the cryptographic process.
Security Concerns and Vulnerabilities of MD5
The MD5 Generator, while instrumental in creating unique checksums to ensure file integrity during transfer, is not without its security concerns. The encryption algorithm behind MD5, which converts data into a fixed-size hexadecimal hash, is critical for secure file verification. However, despite its widespread use in hashing, MD5's vulnerabilities can lead to compromised digital signatures and overall cryptography safety.
Enhanced security measures are necessary, as MD5's algorithm shows susceptibility to collision attacks, which can undermine the data integrity it is meant to protect. The role of the MD5 Generator in maintaining file integrity is pivotal, but it requires caution and an awareness of potential security concerns.
Implementing MD5 in Various Programming Languages
The MD5 Generator, as a cryptographic hash function, ensures data integrity by creating unique checksums. This hashing process converts data into a fixed-size hexadecimal encryption essential for secure file verification. Implementing the MD5 algorithm across various programming languages has standardized digital signature generation, improving overall cryptography practices.
Understanding the MD5 algorithm's role in maintaining file integrity is crucial, especially when detecting alterations during transfers or storage. However, it's also important to be aware of the limitations and security concerns of MD5 encryption, especially in the context of modern cryptographic applications.
Tools and Utilities for Generating MD5 Hashes
The MD5 Generator uses a specific hash function to create a unique checksum to verify file integrity. This hashing process is integral to ensuring data integrity without full encryption. Utilizing a cryptographic algorithm, the MD5 Generator provides a hexadecimal output essential for secure digital signature creation.
The MD5 Generator aids in detecting file tampering, ensuring data integrity through consistent checksum comparison. Its role in file verification is to provide a reliable method for confirming the authenticity of data, a critical aspect of maintaining trust in digital transactions.
Best Practices for Using MD5 for Integrity Checks
One must adhere to certain best practices to ensure the best use of an MD5 Generator for creating a unique hexadecimal checksum. These practices include confirming file authenticity by comparing MD5 hashes pre- and post-transfer, leveraging the algorithm for reliable file verification. While MD5 hashing is not encryption, it provides a digital signature that verifies data integrity without necessarily ensuring confidentiality.
Regular updates and maintenance of your MD5 Generator are essential to protect against vulnerabilities in the MD5 algorithm and to ensure accurate checksums. Educating users on the importance of MD5 checksums is also crucial in preventing tampering and ensuring the integrity of files in transit or storage.
MD5 in Network Security Protocols
The MD5 Generator's hashing capabilities in network security protocols convert data into a unique hexadecimal checksum for secure file verification. The MD5 algorithm's role in cryptography is to ensure the consistency of files by creating a digital signature that is resistant to unauthorized alterations.
Checksums generated by MD5 are vital components in network security, confirming the integrity of files during transfer. Despite its widespread application, the MD5 Generator's vulnerability to collisions necessitates a cautious approach to its role in encryption and data security protocols.
The Future of MD5 and Hashing Technologies
The MD5 Generator, as a tool for creating unique hexadecimal checksums, has been a mainstay in verifying file integrity. However, the future of hashing technologies will likely evolve beyond MD5 to ensure stronger encryption and more robust digital signature protocols. The challenges faced in cryptography, such as MD5's vulnerability to hash collisions, underscore the need for more secure algorithms.
Integrating advanced hash functions into MD5 Generators will be crucial in maintaining the relevance of checksums in file verification. As we look to the future, the role of MD5 and subsequent hashing technologies will be pivotal in protecting data integrity against the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity threats.
Case Studies: MD5 in Action for Data Integrity
Through the implementation of the MD5 Generator, numerous organizations have employed a cryptographic hash function for secure encryption and data integrity assurance. Utilizing MD5 for hashing creates a unique hexadecimal checksum, which is critical for reliable file verification processes. The algorithm's design ensures that even minor changes in data produce distinct hash values, upholding the integrity of the information.
MD5's role in cryptography extends beyond mere hashing to include digital signatures, providing safeguards for authentication and the integrity of documents. Through case studies, we can observe how the implementation of MD5 has enabled organizations to detect tampering, ensuring the integrity of files, whether in transit or storage, thereby maintaining the trustworthiness of their data ecosystems.
FAQ: Your MD5 Generator Questions Answered
1. What is an MD5 generator online?
A web tool that computes the MD5 hash of text or files — no software needed.
2. Is it safe to use online MD5 generators?
Only if they process data in your browser. Avoid tools that upload your data.
3. Can MD5 be cracked?
Not reversed, but brute-forced easily. Use salt and stronger algorithms for security.
4. Does MD5 generate the same hash every time?
Yes — identical input always produces the same hash.
5. How long is an MD5 hash?
128 bits → 32 hexadecimal characters.
6. Can two files have the same MD5?
Yes — this is a collision. MD5 is vulnerable to this.
7. Is MD5 encryption secure?
No — it’s not encryption, and it’s cryptographically broken.
8. How to generate MD5 with salt?
Use HMAC or prepend/append salt: md5(salt + password).
9. What’s the difference between MD5 and SHA256?
SHA-256 is longer (64 chars), more secure, and collision-resistant.
10. Can I generate MD5 for large files?
Yes — tools using WebAssembly handle large files without upload.
Conclusion: Use the Best MD5 Generator Online — Safely & Privately
MD5 is outdated for security, but still useful for file verification and legacy systems.
To stay safe:
- ✅ Use browser-based tools (no upload)
- ✅ Prefer SHA-256 for new projects
- ✅ Always verify file hashes
- ✅ Never store passwords with plain MD5
👉 Try the best tool now: md5 generator online
Author Bio
John Carter – Cybersecurity Engineer & SEO Strategist
15+ years in web security, certified in CISSP and CompTIA Security+. Built hashing tools for Fortune 500 companies. Contributor to OWASP and NIST discussions on cryptographic standards.