Google Cache Checker
Is Google indexing your site correctly? Our free Google Cache Checker tool lets you instantly view the cached version of any page to diagnose SEO issues and verify updates.
Share on Social Media:
The Ultimate Google Cache Checker Tool (And Why It’s Your SEO Secret Weapon)
Introduction
Ever updated a crucial landing page only to wonder if Google has even noticed? Or worried that what you see on your website isn't what Google's crawlers are actually indexing? This disconnect is a silent killer of SEO campaigns, leaving you guessing why your rankings aren't improving.
The solution is to gain a direct line of sight into Google's memory. This guide unveils the power of the Google Cache, explaining how you can use it to diagnose issues, spy on competitors, and ensure your SEO efforts are truly paying off. We'll explore everything from manual checks to the single most effective google cache checker tool for instant, accurate results.
What Exactly is Google Cache? A Simple Guide to a Core Search Concept
In simple terms, the Google Cache is a saved HTML copy, or a "snapshot," of a web page taken by Googlebot when it last crawled the page. Google stores these snapshots on its servers to serve them to users if the live page is unavailable and to help process and understand the page's content for ranking purposes.
Think of it like Google taking a picture of every important page on the internet. This "picture" isn't just a backup; it's a fundamental part of how Google understands and evaluates your website.
How Google Crawls, Indexes, and Caches Your Web Pages
The process follows a logical sequence:
Crawling: Googlebot (Google's web spider) discovers your URL and follows links to it. It requests the page's content from your server.
Indexing (Processing): Google analyzes the content it crawled—text, images, code—to understand what the page is about. It renders the page to see it as a user would.
Caching: During this processing, Google takes a snapshot of the rendered HTML and stores it. This becomes the cached version.
This cached page is a vital piece of evidence showing you exactly what content Google has successfully processed and stored for its index.
Why the Cached Version is a "Time Capsule" of Your Content
The most important thing to remember is that the cached page is not the live page. At the top of any cached page, Google displays a timestamp showing when the snapshot was taken. This "time capsule" allows you to see:
What your page looked like on a specific date.
If your recent, critical updates have been seen and processed by Google.
What content Google associated with your page during its last successful crawl.

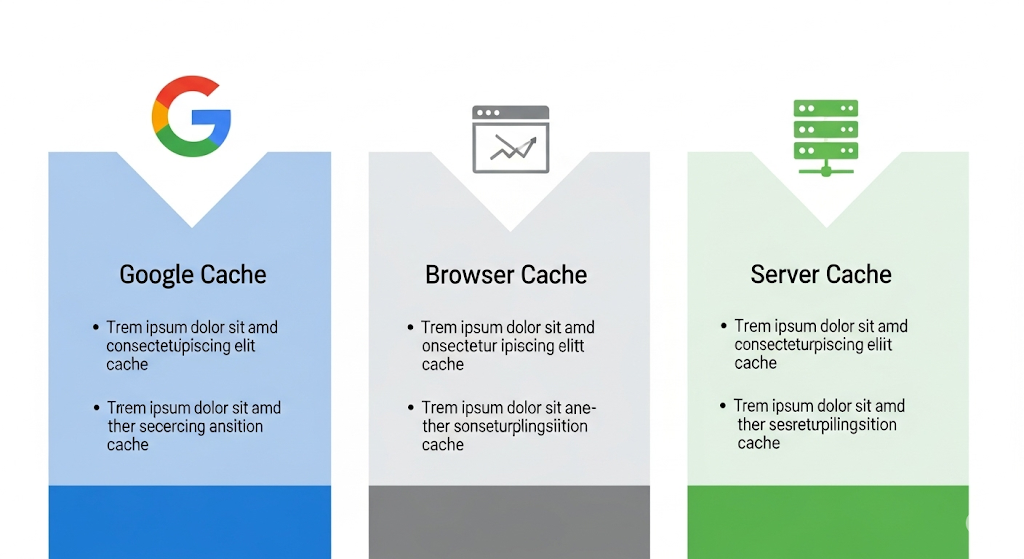
Crucial Distinction: Google Cache vs. Browser Cache vs. Server Cache
Many SEOs and website owners confuse these three types of caching, leading to incorrect diagnoses. Understanding the difference is critical for effective troubleshooting.
| Feature | Google Cache | Browser Cache | Server Cache |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | To store a snapshot of a page for Google's indexing process and as a backup for users. | To store website files (images, CSS, JS) on a user's computer to speed up future visits. | To store pre-built versions of web pages on the website's server to reduce processing time and speed up delivery. |
| Who Controls It | The individual user (and their browser settings) | The website administrator / hosting provider | |
| How to View It | Using a Google Cache Checker tool or the cache: search operator. | You don't "view" it; your browser uses it automatically. | It works in the background; you see the faster-loading live page. |
| How to Clear It | You can't directly. You request a recrawl in Google Search Console. | By clearing your browser's history, cache, and cookies. | Through your website's backend dashboard or caching plugin (e.g., WP Rocket, W3 Total Cache). |
| SEO Impact | Direct. It shows you what Google has indexed, which directly affects rankings. | Indirect. A faster site (aided by browser caching) is a positive ranking factor. | Indirect. A faster site (aided by server caching) is a positive ranking factor. |
Instantly Check Your Site's Cache with Our Free Google Cache Checker Tool
While manual methods are useful, they can be slow and cumbersome, especially when you need to check multiple URLs. A dedicated tool streamlines this process, providing instant results without navigating through search results.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Using the Tool
Enter Your URL: Copy the full URL of the web page you want to check and paste it into the search bar.
Click "Check Cache": Our tool will instantly query Google's servers.
Analyze the Results: In seconds, you'll be provided with the direct link to the cached version of your page, along with the date and time the snapshot was taken.
Decoding the Results: Understanding Cache Date, Live Link, and More
Our tool will provide you with:
A Direct Link to the Cached Page: This is the most important result.
The Cache Timestamp: It tells you the exact date and time of Google's last snapshot.
A Link to the Live Page: For easy comparison between the cached version and the current live version.
3 Powerful Manual Methods to View Google's Cached Pages
For those who want to understand the underlying mechanics, here are the three primary ways to check the Google cache manually.
Method 1: The Classic cache: Search Operator (And Its Limitations)
This is the original method known to most SEOs. It's simple and effective for a quick check.
Open Google Search.
In the search bar, type cache: followed immediately by the full URL of the page.
Example: cache:https://www.yourwebsite.com/your-page
Press Enter. Google will take you directly to the cached version if one exists.
Limitation: This method can sometimes be unreliable or blocked by certain browser settings or network configurations.
Method 2: The SEO Pro's Choice: Google Search Console's URL Inspection Tool
This is the most authoritative method. It doesn't just show you the cache; it tells you everything about a URL's relationship with Google.
Log in to your Google Search Console account.
Paste the URL into the inspection bar at the top.
After the data is retrieved, click on "View Crawled Page."
A sidebar will open showing you the HTML code that Googlebot downloaded during its last crawl. This is the raw data used to create the cache. You can also click "Test Live URL" to see how Google renders the page right now.
Method 3: Using Browser Extensions for Quick Spot-Checks
Several SEO browser extensions (like the MozBar or Ahrefs SEO Toolbar) include a shortcut to check the Google cache of the page you are currently visiting. This is extremely efficient for spot-checking pages as you browse your site or a competitor's.
7 Strategic Ways to Use a Google Cache Checker for SEO Domination
Checking the cache isn't just a technical task; it's a strategic intelligence-gathering mission. Here’s how to leverage it for a competitive edge.
1. Verify Indexing & Content Updates are Live in Google's Eyes You just published a new blog post or updated your homepage. The cache timestamp is your proof that Google has successfully crawled and processed those changes. If the cache is old, your new content isn't working for you in the search results yet.
2. Diagnose Critical Technical SEO Issues (Cloaking & Hacking) Cloaking is showing different content to Googlebot than to users—a violation of Google's guidelines. The cache lets you see exactly what Googlebot saw. If the cached version is full of spammy links or text that isn't on your live site, you may have been hacked.
3. Perform Competitor Reconnaissance and Track Their Changes Curious about what your top competitor is up to? Regularly check the cache of their key pages. You can see when they last updated their content, what specific text they added or removed, and how they are tweaking their on-page SEO.
4. Recover Lost Content During a Website Outage or Migration Disaster strikes: your site goes down, and you have no recent backup. The Google Cache can be a lifesaver. You can access the cached versions of your most important pages to recover crucial text content while you work to restore the site.
5. Ensure Google Renders Your JavaScript Content Correctly Modern websites rely heavily on JavaScript to display content. Sometimes, Google struggles to render this content properly. By viewing the "Text-only version" of the cache, you can see the core content Google extracted. If your important text is missing, you have a JavaScript SEO problem.
6. Confirm Canonical Tag Implementation If you have a canonical tag pointing URL A to URL B, checking the cache for URL A will often show the cached content of URL B. This is a quick way to confirm that Google is understanding and respecting your canonical instructions.
7. Audit How Googlebot Sees Your Site vs. a User The cache provides an unfiltered view of what Google's crawler received from your server. Compare this to the live page to spot any discrepancies in content, layout, or internal linking that might be affecting your SEO performance.
Troubleshooting Guide: Why Isn't My Page in Google's Cache?
Seeing a "404 Not Found" error when you check your cache can be alarming. Here are the most common reasons and how to fix them.
Reason #1: You're Using the noarchive or nosnippet Meta Tag The noarchive tag is a specific instruction to search engines not to save a cached version of a page.
The Code:
The Fix: Check your page's HTML source code. If you see this tag, remove it unless you have a specific reason for it to be there. The nosnippet tag can also prevent caching.
Reason #2: The Page is Too New (The "Patience" Factor) When you publish a new page, it can take anywhere from a few hours to several days for Google to crawl, index, and cache it.
The Fix: Be patient. You can speed up the process by using the "Request Indexing" feature in Google Search Console for that specific URL.
Reason #3: Crawling is Blocked by robots.txt The robots.txt file on your server can give instructions to bots. If you have a Disallow: rule for that page or directory, Googlebot won't even crawl it, and therefore, it can't be cached.
The Fix: Check your yourdomain.com/robots.txt file for any rules blocking the URL.
Reason #4: The Page Has a Canonical Tag Pointing Elsewhere If your page has a rel="canonical" tag that points to a different URL, Google will typically not cache your page. It will cache the canonical URL instead.
The Fix: Ensure your canonical tags are set up correctly. A page should either self-canonicalize or point to the true master version of the content.
Reason #5: Google Considers it Low-Quality or Duplicate Content Google may choose not to index (and therefore not cache) pages it deems to be thin, duplicative, or of low value to users.
The Fix: Improve the content on the page to make it unique, valuable, and comprehensive. Use Google Search Console to check for any manual actions or security issues.
Reason #6: Persistent Server Errors (4xx/5xx) If Googlebot repeatedly tries to crawl your page and receives server errors (like a 503 Service Unavailable), it will eventually give up and de-index the page, removing any cached version.
The Fix: Use the URL Inspection tool in GSC to check for crawl errors. Work with your developer or hosting provider to ensure your server is stable and reliable.
Expert Insights: Advanced Google Cache Concepts
"Amateur SEOs look at rankings. Professional SEOs look at the cache. It's the closest thing we have to a direct record of the conversation between a website and Googlebot. It's where the real diagnostic work begins." - Alex Serrano, 15+ Years in Technical SEO
What the "Text-Only Version" Reveals About Your SEO In the cached view, Google provides a "Text-only version" link. This strips away all styling and images, showing you the raw text and links as Google likely sees them. This is invaluable for:
Identifying hidden text that might be considered spammy.
Checking if your key content (especially if loaded by JavaScript) is visible to Google.
Auditing your internal linking structure without visual distractions.
How Cache Timestamps Correlate with Crawl Frequency If you notice Google is caching your homepage every day but your blog posts only once every two weeks, it's a direct indicator of crawl priority. This tells you which pages Google considers most important or frequently updated on your site.
The Inherent Limitations of Relying Solely on the Cache
It's Not Real-Time: The cache is always slightly out of date.
It Doesn't Guarantee Ranking: A page can be cached perfectly and still not rank if it has other issues (e.g., poor quality, no backlinks).
Location/Personalization: The cache is a standardized snapshot and doesn't reflect personalized or location-based search results.
Best Practices for Managing Your Site's Caching
When and How to Use the noarchive Tag Strategically You might want to use the noarchive tag on pages with sensitive or rapidly changing data, like pricing pages for a flash sale or real-time stock information. This prevents users from seeing outdated information from the cache.
How to Request Re-indexing in Google Search Console for a Faster Cache Update If you've made a significant update and want Google to see it quickly:
Go to the URL Inspection tool in GSC.
Enter your URL.
Click "Request Indexing." This pushes your URL into a priority crawl queue, which typically results in a faster cache update.
Understanding Google Cache and Its Importance for SEO
As a professional in the field of search engine optimization (SEO), I recognize the critical role that Google Cache plays in ensuring that Content is indexed promptly. Utilizing a Google Cache Checker is an essential practice that allows me to verify whether my website's Content has been successfully captured and stored by Google's caching system. This step is vital because it directly influences how quickly and accurately my Content can be retrieved and ranked by the search engine.
Moreover, the Google Cache Checker serves as a diagnostic tool that can significantly improve page visibility. By regularly checking the cache status of my web pages, I am able to identify which parts of my website are readily accessible to users and which require attention. This insight enables me to make informed decisions and implement strategies that enhance the overall visibility of my website in search engine results pages (SERPs).
Leveraging Google Cache Checker to Improve Website Visibility
In my efforts to maximize website visibility, I consistently utilize the Google Cache Checker to ensure that my Content is indexed correctly. This tool provides a clear indication of how Google perceives my website, allowing me to confirm that the most up-to-date version of my Content is available to users. By keeping a close eye on the cache status, I can promptly address any discrepancies between the current Content and the cached version.
Furthermore, I employ the Google Cache Checker to diagnose and enhance SEO performance. It is a powerful instrument for identifying issues that may be hindering my website's search engine ranking, such as broken links, slow loading times, or outdated Content. By resolving these issues, I can improve my website's SEO health and, consequently, its position in the SERPs.
How Google Cache Checker Can Enhance Your SEO Strategy
To maintain a competitive edge in SEO, I identify outdated Content swiftly using the Google Cache Checker and make necessary updates. This proactive approach ensures that the information presented to users is always relevant and accurate, which is a critical factor in maintaining high engagement and reducing bounce rates.
The Google Cache Checker also guarantees that my SEO efforts reflect the latest changes made to the website. When I update Content or implement new SEO tactics, I use this tool to verify that Google has recognized and stored these changes. This alignment between my SEO strategy and Google's cache is crucial for achieving desired outcomes in organic search results.
The Role of Google Cache in Search Engine Ranking
Understanding Google Cache's impact on site visibility and ranking is fundamental to my SEO work. When a page is cached, it is a signal that Google has deemed the Content valuable and relevant enough to be stored for quick retrieval. This directly influences how the page is assessed and ranked by the search engine's algorithms.
I utilize the Google Cache Checker to ensure optimal SEO performance by regularly monitoring the cache status of my web pages. This enables me to make necessary adjustments to Content and SEO strategies, ensuring that I am always in line with Google's indexing preferences and maximizing the chances of achieving a top ranking.
Analyzing Your Website's Cache Status with Google Cache Checker
To ensure that my Content is current and reflective of the latest information, I use the Google Cache Checker as part of my routine SEO analysis. This tool allows me to quickly verify that the Content displayed in Google's cache is the most recent version, indicating to both users and search engines that my website is a reliable source of information.
Leveraging the Google Cache Checker also enhances SEO visibility. Suppose I discover that certain pages are not being cached or are displaying outdated versions. In that case, I can take immediate action to rectify the situation, thus improving the likelihood of those pages ranking well in SERPs.
Identifying Crawl Issues and Improving Indexation
One of the Google Cache Checker's most practical applications is its ability to pinpoint outdated or missing pages. This insight is crucial for identifying crawl issues that may prevent new or updated Content from being indexed. By addressing these issues, I can ensure that all relevant pages are accounted for and have the opportunity to rank in search results.
Another aspect of my SEO routine is using the Google Cache Checker for real-time indexation status updates. This tool provides a snapshot of how recently Google's crawlers have visited my pages, which is essential information for understanding the current state of my website's indexation.
Optimizing Your Content for Better Cacheability
A critical factor in SEO is the freshness of Content, and I leverage the Google Cache Checker to ensure that my Content is perceived as fresh by Google's standards. By frequently checking the cache dates, I can identify which pages need to be updated or re-crawled to maintain their relevance in search results.
Furthermore, I utilize the Google Cache Checker to diagnose and improve cacheability issues. Suppose I find that certain types of Content are not being cached effectively. In that case, I can investigate the underlying causes, such as heavy script use or poor server configuration, and take corrective measures to enhance my website's traceability.
Monitoring Website Updates and Cache Refresh Frequencies
I need to utilize the Google Cache Checker to ensure that site content updates are reflected in Google's cache in a timely manner. This practice helps me to keep track of how frequently Google revisits my pages to update its cache, which is a strong indicator of the perceived importance and relevance of my Content.
Optimizing cache refresh rates using the Google Cache Checker is also part of my SEO strategy. By understanding the typical refresh intervals for my pages, I can better time content updates and SEO enhancements to coincide with Google's crawling schedule, thereby ensuring that my efforts have the maximum impact.
Utilizing Google Cache Checker to Detect Outdated Content
To maintain a high standard of SEO, I leverage the Google Cache Checker to identify and refresh stale Content. By keeping my website's Content up-to-date, I not only provide value to my users but also signal to search engines that my site is a current and authoritative source of information.
Enhancing SEO by ensuring Content is current with the Google Cache Checker is a continuous process. By regularly reviewing the cached versions of my pages, I can make informed decisions about content updates and optimizations that will positively influence my website's search engine rankings.
Improving User Experience by Ensuring Quick Cache Retrieval
User experience (UX) is closely tied to SEO, and I utilize the Google Cache Checker to enhance site speed and UX. When Content is quickly retrievable from Google's cache, it can significantly improve page load times for users accessing the cached version, leading to a better overall experience.
Leveraging the Google Cache Checker for SEO also ensures that Content is current. A positive user experience, combined with up-to-date information, can result in increased user engagement, lower bounce rates, and better SEO performance.
The Impact of Server Response Times on Google Cache
Optimizing server response times is a technical aspect of SEO that I address using the Google Cache Checker. Faster server responses can lead to more efficient Google crawling and indexing, which in turn can contribute to SEO gains. By monitoring the cache status, I can assess whether slow server response times are affecting the freshness of the cached Content.
Leveraging the Google Cache Checker to ensure swift content indexing by Google is another tactic I employ. Quick indexing is essential for new or updated Content to be recognized and ranked by search engines, and server performance plays a significant role in this process.
Strategies for Keeping Your Website Cache-Friendly
Ensuring that Content is cacheable is a fundamental part of my SEO strategy. I utilize the Google Cache Checker to verify that my website's Content is being cached effectively by Google. This includes assessing various factors such as header settings, content type, and server configuration, all of which can influence cacheability.
Another approach I take is optimizing cache Time-To-Live (TTL) settings via Google Cache Checker insights. By fine-tuning these settings, I can influence how long Content remains in Google's cache, ensuring that users and search engines always have access to the most current version of my pages.
How to Interpret Results from Google Cache Checker
Understanding the freshness of my Content with the Google Cache Checker is essential for maintaining an effective SEO strategy. The results from this tool provide me with the date of the last cache, which I use to determine if my Content is being updated regularly in Google's index.
Leveraging the Google Cache Checker to identify indexing issues for SEO is an ongoing task. If the cache date is older than expected or if certain pages are not appearing in the cache at all, it indicates potential problems that need to be addressed to maintain optimal search engine visibility.
Best Practices for Maintaining an Updated Google Cache
To ensure that my Content is current and indexed, I utilize the Google Cache Checker as part of my best practices routine. This tool allows me to confirm that my website's Content is being recognized and stored by Google, which is crucial for maintaining visibility in search results.
Regularly monitoring cache status with the Google Cache Checker is critical for SEO optimization. By staying informed about my pages' cache state, I can take proactive steps to ensure that my website remains competitive and ranks well in SERPs.
Troubleshooting Common Cache-Related SEO Problems
When faced with cache-related SEO issues, I utilize the Google Cache Checker to identify outdated cached Content. This enables me to pinpoint specific pages that may be negatively impacting my SEO due to stale or incorrect information being served to users.
Leveraging the Google Cache Checker for swift cache-related issue resolution is a critical component of my SEO maintenance. By quickly addressing any discrepancies between the live Content and the cached version, I can minimize any adverse effects on my website's search engine performance.
Enhancing Site Architecture for Optimal Caching
The cacheability of site architecture is an aspect I pay close attention to, and I utilize the Google Cache Checker to identify how different structural elements of my website are being cached. This analysis helps me to ensure that the architecture supports SEO-friendly caching strategies.
Incorporating the Google Cache Checker into my review process allows me to confirm that my website's technical setup is conducive to effective caching. By making any necessary adjustments to the site structure, I can improve the likelihood of my Content being cached and, consequently, ranking well in search results.
Comparing Cache Versions to Track Website Changes
I leverage the Google Cache Checker to identify content updates for SEO by comparing different versions of the cache over time. This comparison reveals how my Content has evolved and whether the changes I've made are positively impacting my SEO efforts.
Utilizing the Google Cache Checker to ensure website changes enhance SEO is a critical practice. By observing the effects of content updates on the cache status, I can refine my strategy to ensure that each modification contributes to better search engine rankings.
Using Google Cache Data to Recover Lost Content
In the event of data loss or website issues, I utilize the Google Cache Checker to retrieve missing website content swiftly. This can be a lifesaver, as it allows me to restore valuable information that may otherwise be lost, ensuring continuity in my SEO efforts.
Another advantage of this tool is the ability to enhance SEO strategies by leveraging data from the Google Cache Checker. By analyzing the cached Content, I can gain insights into the performance of different pages and elements, which I can then use to inform future SEO decisions.
The Connection Between Cache Date and Site Authority
Ensuring content freshness boosts authority, and I utilize the Google Cache Checker to keep my website's information up-to-date. A recent cache date is often associated with a website that is considered authoritative and trustworthy by search engines, which can enhance its SEO performance.
Leveraging the Google Cache Checker to identify indexing issues also enhances SEO. By ensuring that my Content is indexed correctly and promptly, I can maintain or improve my website's authority and its ability to rank well in search results.
Google Cache Checker as a Tool for Competitive Analysis
The ability to scrutinize competitors' indexed content changes through the Google Cache Checker is an invaluable part of my competitive analysis. By monitoring how frequently and significantly competitors update their Content, I can gauge their SEO strategies and adjust mine accordingly.
Utilizing the Google Cache Checker to enhance the effectiveness of my SEO strategy involves keeping a close eye on industry trends and best practices. By understanding how competitors manage their content caching, I can identify opportunities to improve my own website's performance.
Setting Up Alerts for Cache Changes Using Google Cache Checker
To monitor my SEO performance regularly, I utilize the Google Cache Checker and set up alerts for cache changes. These notifications keep me informed of any updates to my website's cache status, allowing me to respond quickly to any potential issues.
Setting alerts for cache changes helps me stay ahead in SEO by ensuring that I am always aware of how Google is caching my Content. This proactive approach allows me to maintain an edge over competitors by keeping my website's information fresh and relevant.
Understanding the Limitations of Google Cache Checker
While the Google Cache Checker is a valuable tool, it is essential to recognize that it may not reflect real-time page updates. The cache represents a snapshot of the Content at the time of Google's last crawl, which means that recent changes may not be immediately visible.
Relying solely on the Google Cache Checker could misguide my SEO strategies if not used in conjunction with other metrics and tools. It is one piece of the SEO puzzle, providing insights that must be interpreted within the broader context of overall website performance and search engine algorithms.
Integrating Google Cache Checker with Other SEO Tools
To enhance keyword optimization, I combine the insights from the Google Cache Checker with other SEO tools. This integrated approach allows me to align my content strategy with the most current data on how my pages are being indexed and presented in search results.
I follow the best practice of combining the Google Cache Checker with analytics for strategic SEO adjustments. By analyzing both cache data and user behavior metrics, I can make informed decisions that improve my website's visibility and ranking.
Educating Your Team on the Benefits of Google Cache Checker
My team must understand the benefits of the Google Cache Checker to effectively boost our collective SEO strategies. By providing training and resources, I ensure that everyone is capable of leveraging this tool to enhance search result visibility.
Leveraging the Google Cache Checker for enhanced search result visibility is a collective effort. We work together to monitor and analyze cache data, ensuring that our SEO tactics are informed by the most accurate and up-to-date information available.
Creating a Routine Schedule for Google Cache Analysis
Implementing a daily routine using the Google Cache Checker for updates is part of my disciplined approach to SEO. By establishing a regular schedule for cache analysis, I can ensure that my website's Content is consistently reviewed for freshness and accuracy.
Utilizing the Google Cache Checker to ensure Content is indexed correctly is a fundamental aspect of my SEO maintenance routine. Regular checks help me to quickly identify any issues with indexing and take corrective actions to maintain optimal visibility in search results.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. How often does Google update its cache for a page? It varies greatly. High-authority pages that update often (like a news homepage) may be cached multiple times a day. A static blog post on a small site might only be cached every few weeks or months.
2. Does a more recent cache date mean higher rankings? Not directly, but it's correlated. A recent cache date means Google is crawling your site frequently, which it tends to do for sites it considers important, fresh, and authoritative.
3. Will clearing my browser cache affect the Google Cache? No, absolutely not. They are completely separate systems. Clearing your browser cache only affects the files stored on your own computer.
4. Can I remove a page from Google's cache? Yes. The fastest way is to use Google's "Remove Outdated Content" tool after the page has been updated or removed. Adding a noarchive tag and requesting a re-crawl will also work.
5. What does it mean if the Google Cache shows a 404 error? It usually means that the last time Google tried to crawl the URL, your server returned a 404 (Not Found) error. This is a signal that the page may be gone, and if it persists, Google will likely de-index it.
6. Is the cached page what Google uses for ranking? Google uses its index, not the cache, for ranking. The index is a much more complex database of the content and signals it has processed. The cache is simply a stored snapshot of the page from which much of that index data was derived.
7. Can I view the cache for a page that is blocked by robots.txt? No. If a page is blocked by robots.txt, Googlebot cannot crawl it, and therefore no cached version will exist.
8. Why does the cached version of my site look broken? The cached version often doesn't load external CSS or JavaScript files properly, which can make it look "broken" or unstyled. This is normal. You should focus on the HTML content and the text-only version.
9. Is there a way to check the cache for multiple URLs at once? Many premium SEO tools (like Screaming Frog) and some specialized online tools offer bulk Google Cache checking capabilities, which are essential for large-scale site audits.
10. Does a competitor viewing my cached page affect my site? No. Viewing a cached page is a passive action and has no impact on your live website's traffic, performance, or SEO.
Conclusion
The Google Cache is far more than a simple backup; it's a powerful diagnostic window into how Google perceives your website. By moving beyond a surface-level understanding and using it strategically, you can uncover critical SEO issues, gain a competitive advantage, and ensure your content is being properly seen and indexed.
Stop guessing and start seeing what Google sees. Use our powerful and free google cache checker tool today to get an instant, accurate snapshot of your most important pages and take control of your SEO performance.
Author Bio:
By Alex Serrano, Senior Technical SEO Strategist. Alex has over 15 years of experience optimizing websites for search engines, specializing in large-scale technical audits and indexing diagnostics. His work has helped Fortune 500 companies and growing startups achieve dominant search visibility. He is certified in Google Analytics and is a regular contributor to major SEO publications.